Images
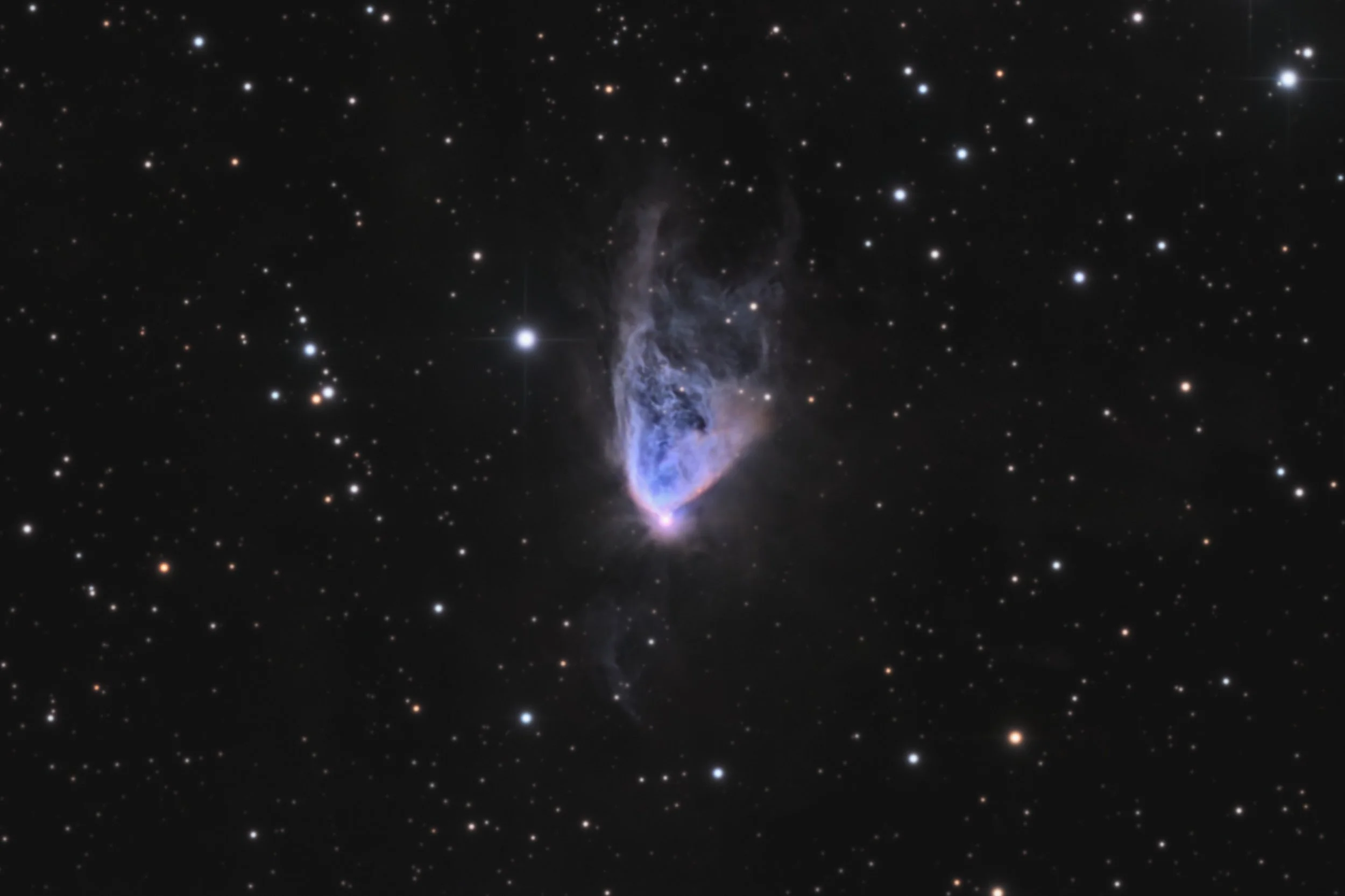
Caldwell 46
Caldwell 46, also known as NGC 2261 or Hubble’s Variable Nebula is a variable nebula located in the constellation Monoceros. It got its nickname from observations that Edwin Hubble did during the middle of the previous century, in which he discovered that both shape and brightness changes over time. One explanation is that dark clouds block light from the central illuminating star from time to time, in a timespan of weeks or months.
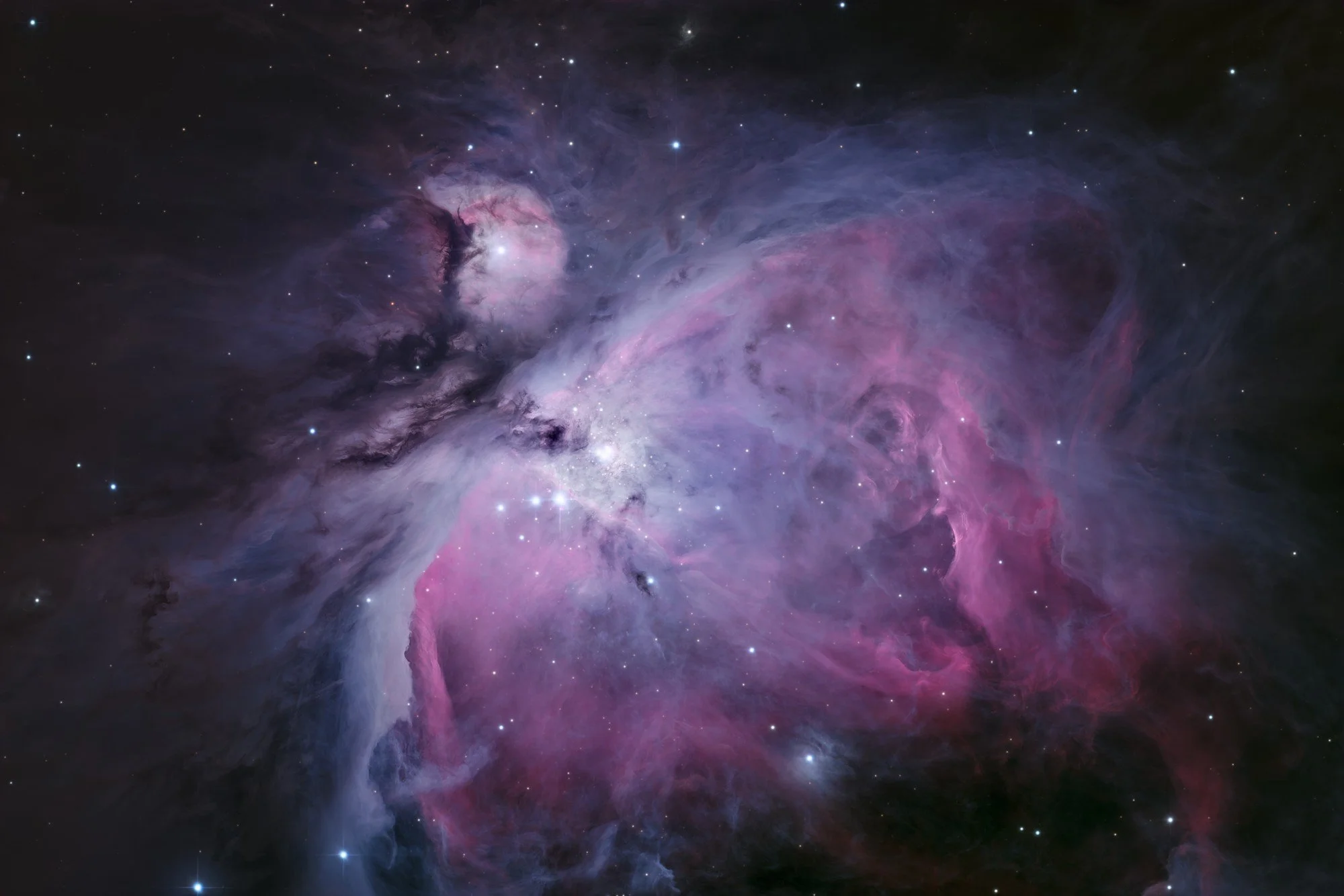
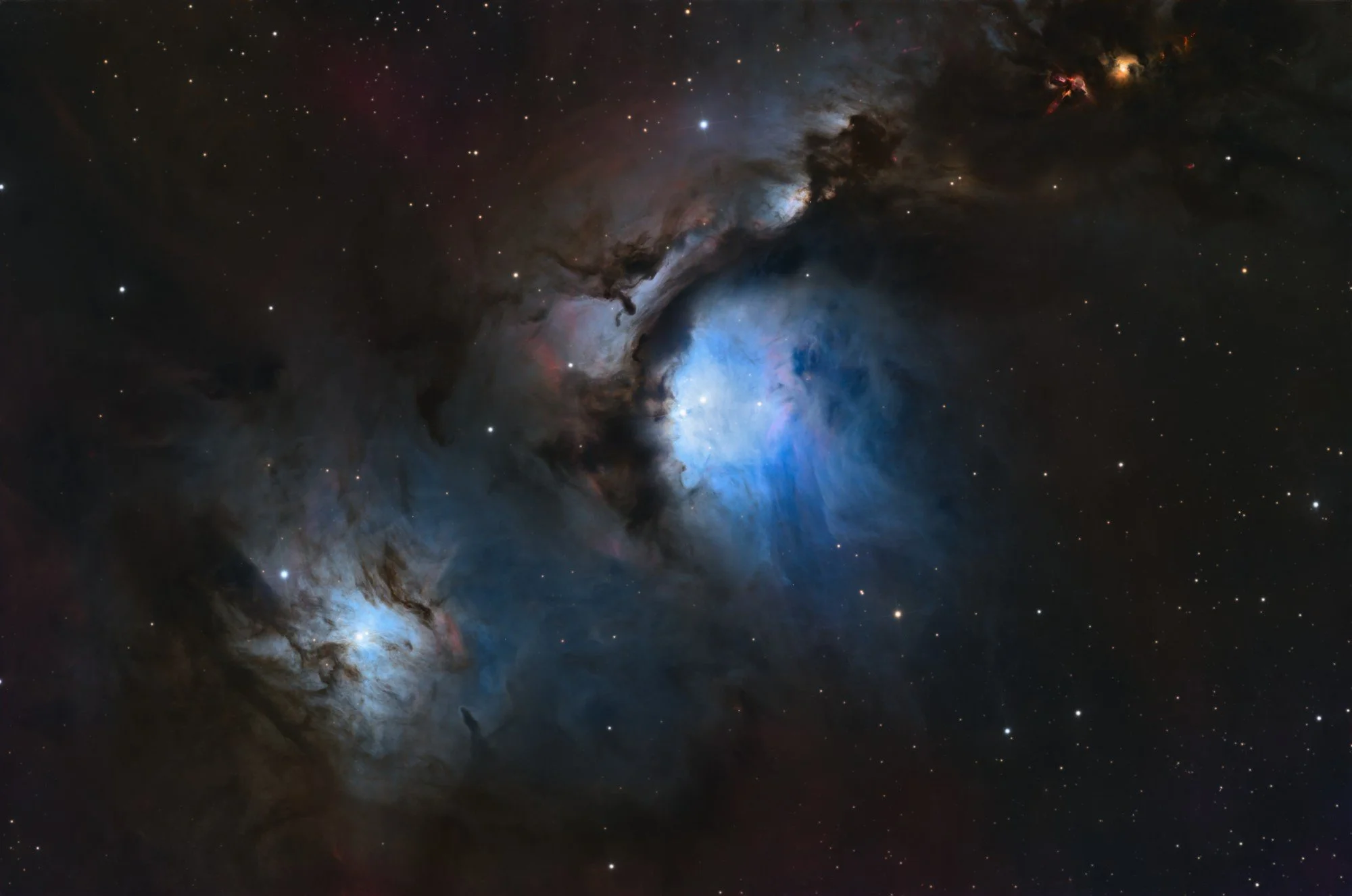
M42 | M43
The Orion Nebula is one of those iconic objects that wants to be in any astrophotographers portfolio. This object was the first image taken here at AstroWorldCreations, back in 2018. A lot has changed since then, and a revisit of this impressive nebula was long overdue. While M42 is the actual Orion Nebula, the neighbouring M43 is always shot in the same image, but goes by the name or Mairan’s Nebula.
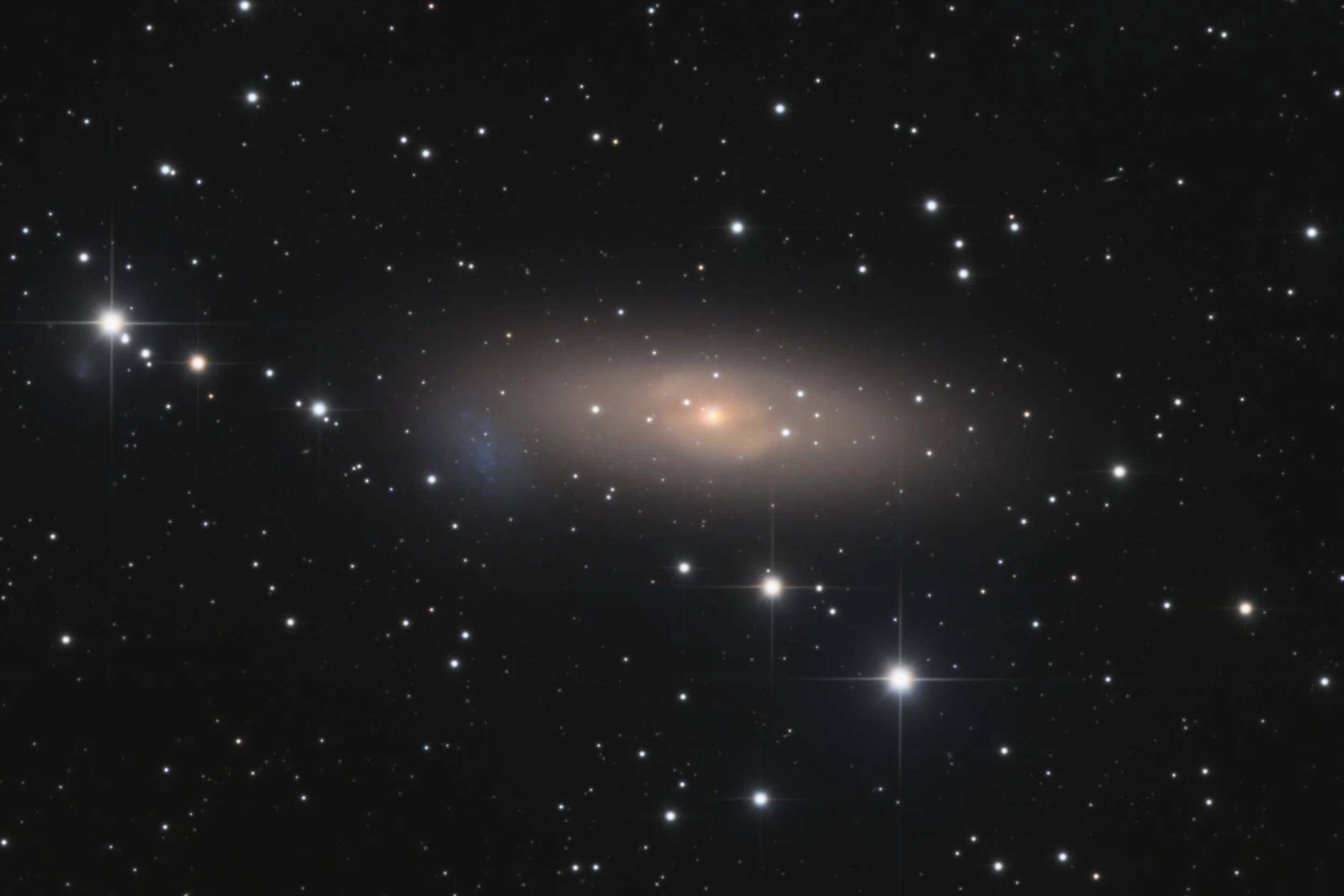
Arp 135
Arp 135, also known as NGC 1023 or the Perseus Lenticular Galaxy, is a member of the NGC 1023 group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. Distance measurements vary from 30 to 64 million light-years. Arp classifies this object under “Galaxies with Nearby Fragments". Arp 135 is a barred lenticular galaxy, with a barred spiral structure still visible in an otherwise elliptical structure. Both the barred structure and the accompanying (blue-ish) satellite galaxy NGC1023A are well visible in this image.
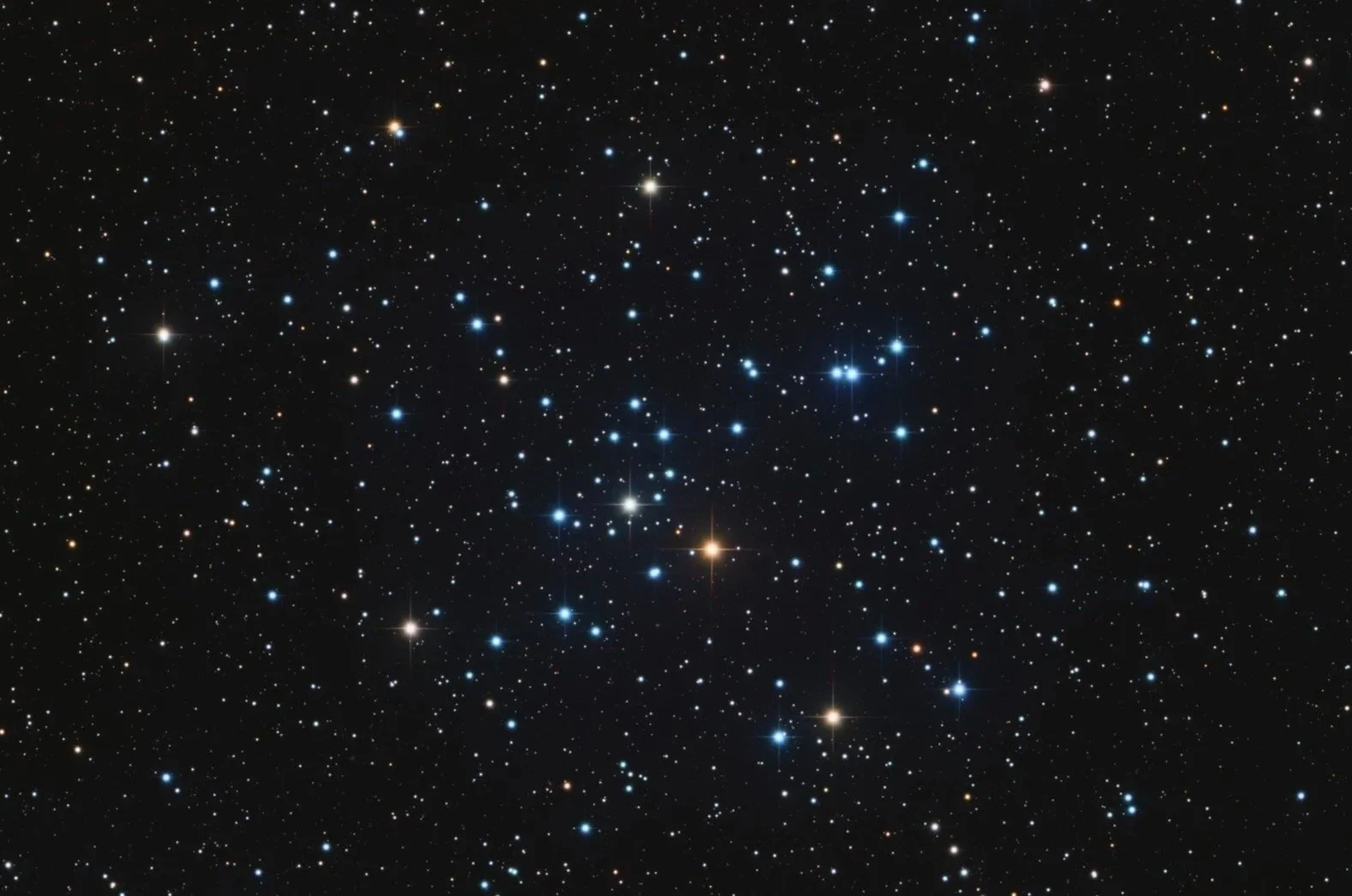
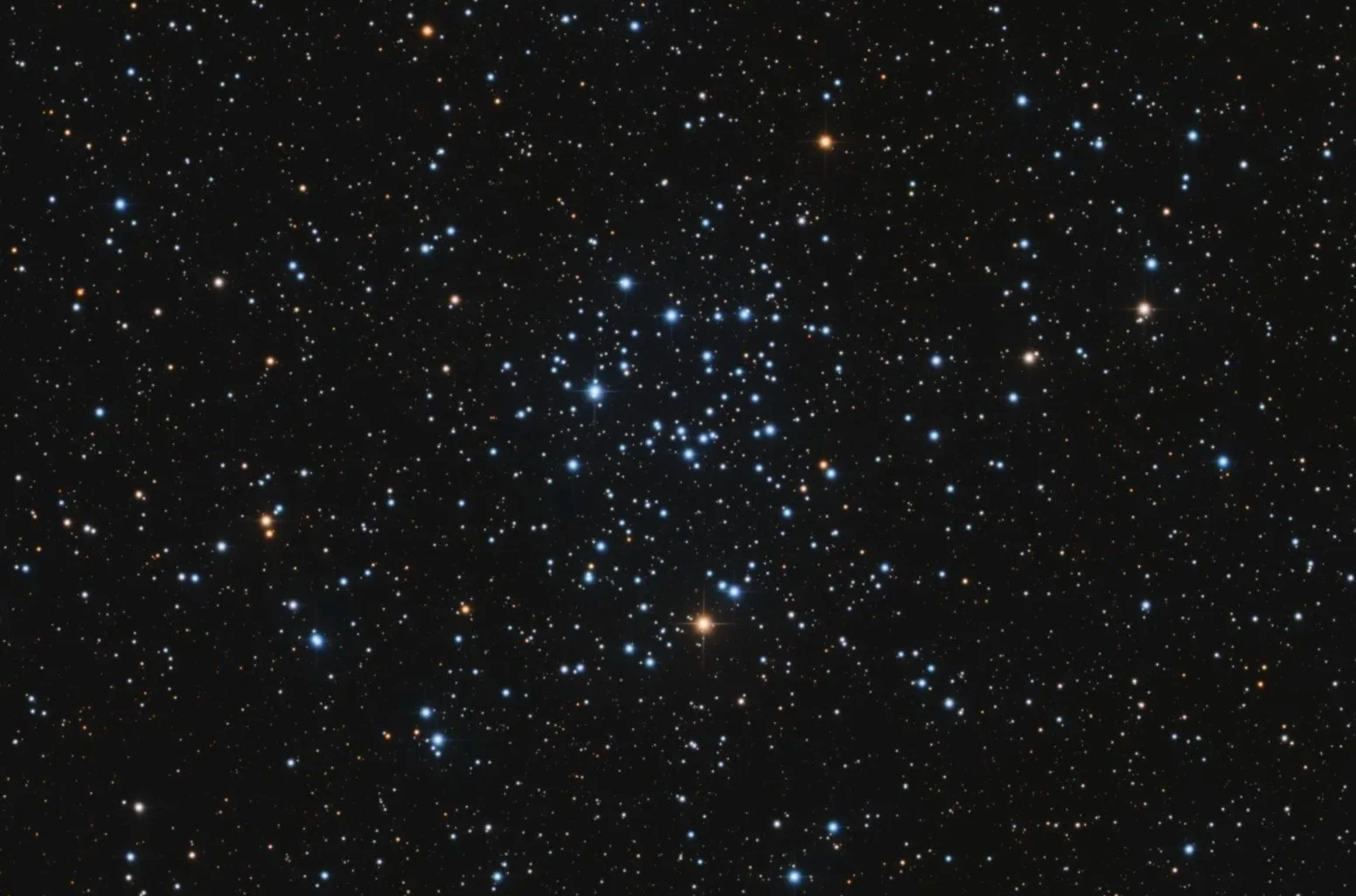
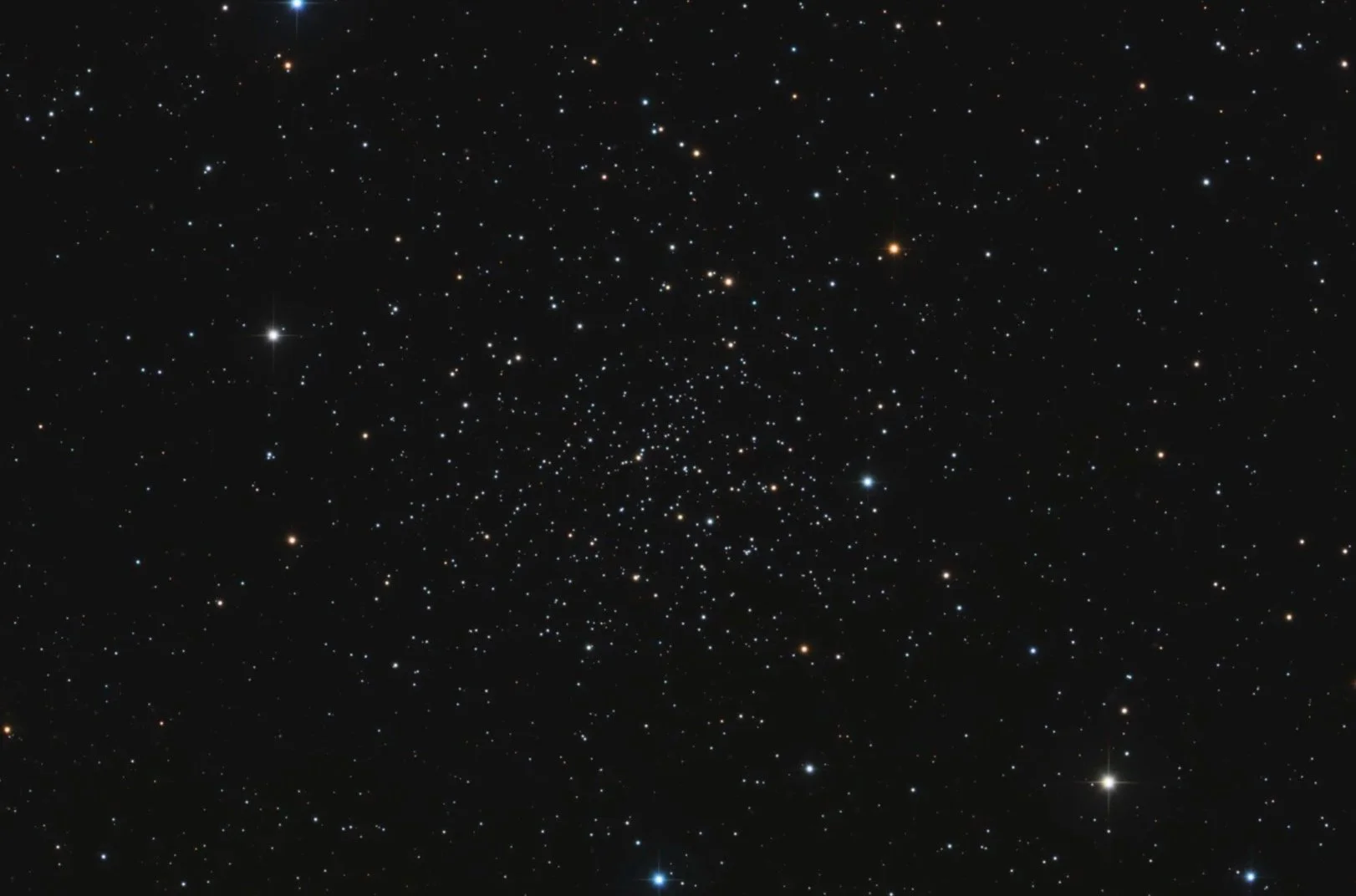
M41
Messier 41 is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major. The cluster spans an area comparable to the size of the full moon and contains about 100 stars, including several red giants and white dwarfs. Discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654, M41 may have been observed by Aristotle as early as 325 BC. It is sometimes called the Little Beehive Cluster due to its resemblance to the Beehive Cluster (M44).
M78
M78 is a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. It is the brightest diffuse reflection nebula in a group that includes NGC 2064, NGC 2067, and NGC 2071, all part of the Orion B molecular cloud complex. M78 is located approximately 1,350 light-years from Earth. M78 was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780, and included in Charles Messier's catalog of comet-like objects that same year.
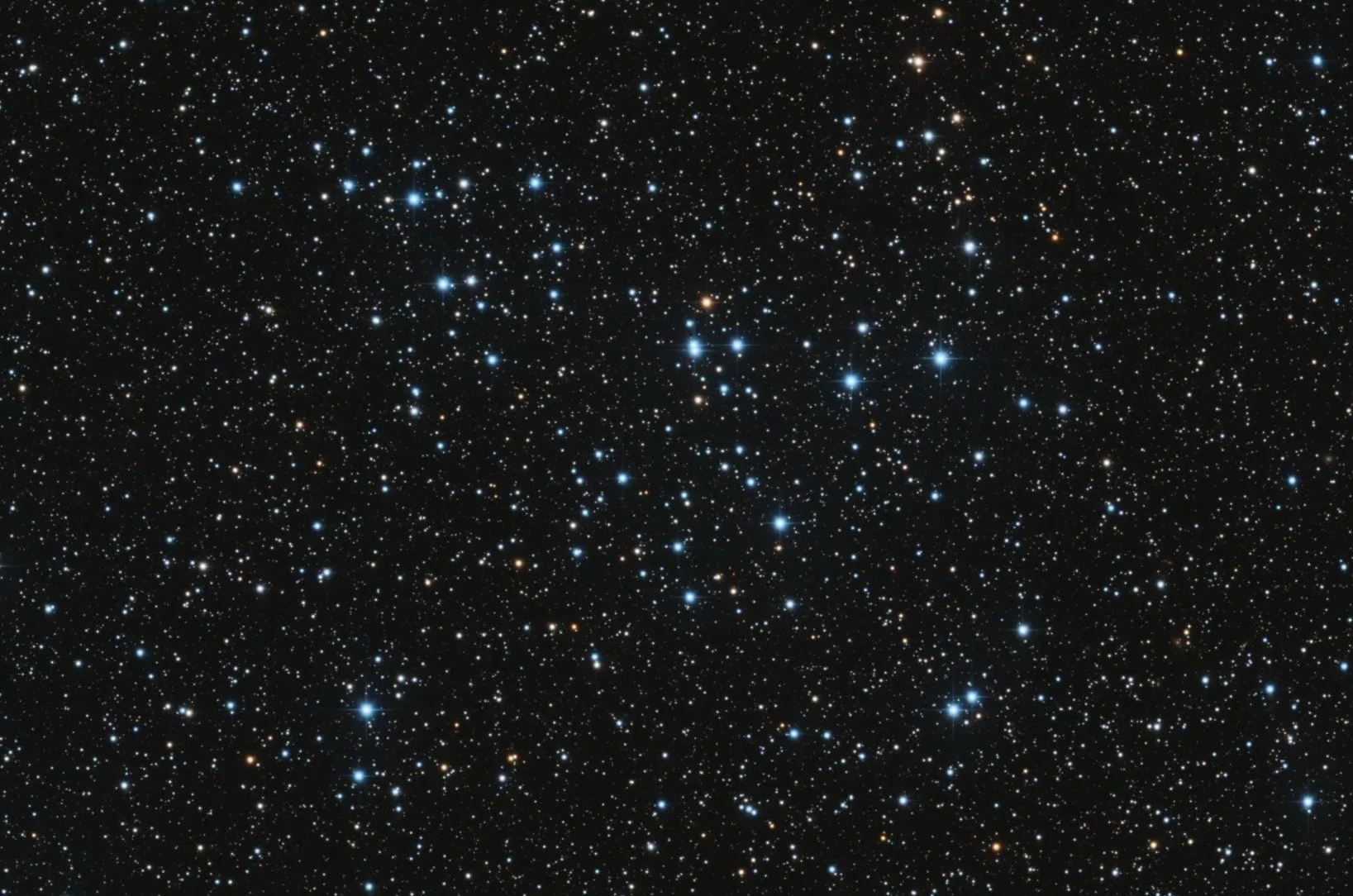
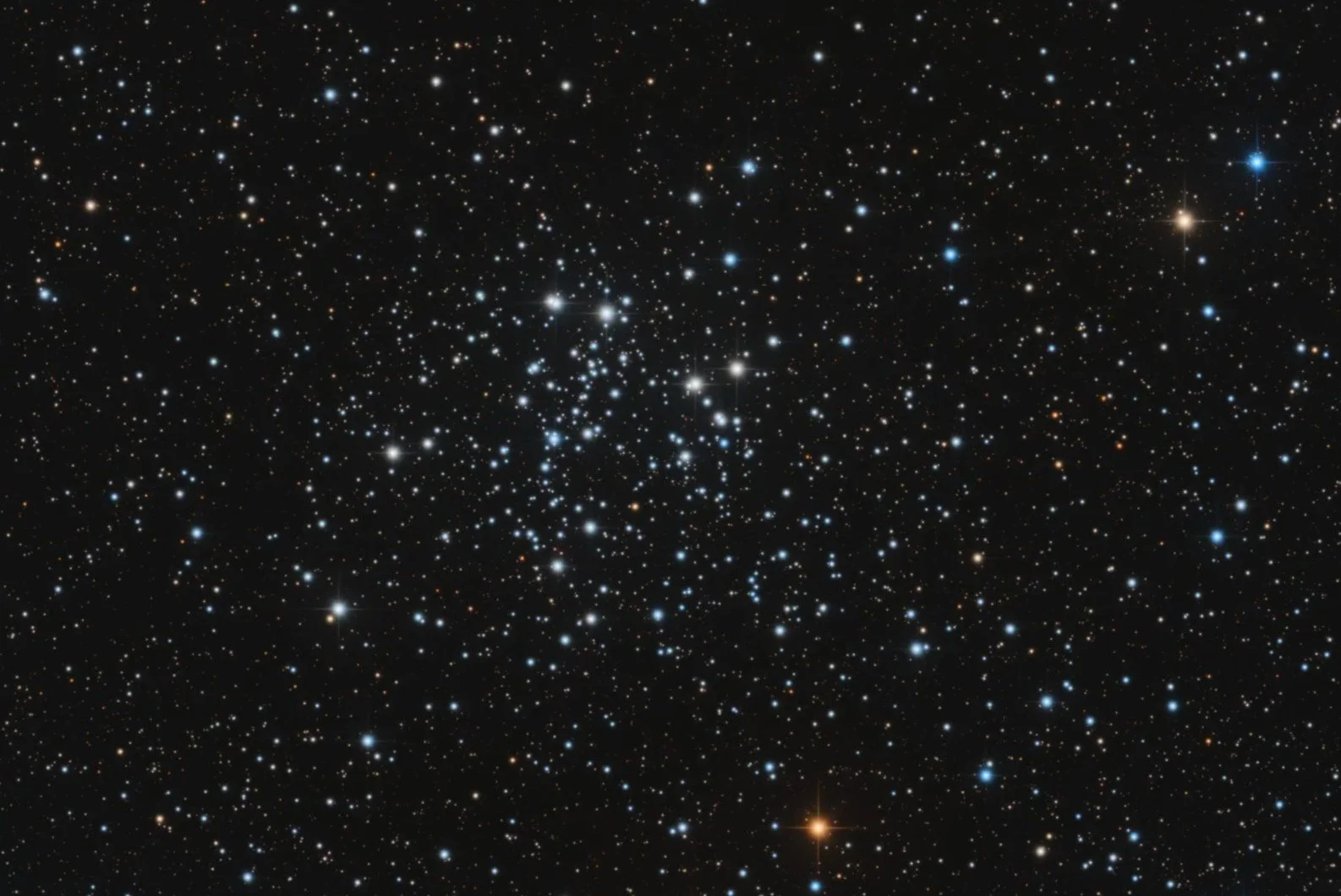
M50
Messier 50, also known as NGC 2323 or the Heart-shaped Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Monoceros. It was recorded by G. D. Cassini before 1711 and independently discovered by Charles Messier in 1772 while observing Biela's Comet. M50 is about 2,900 light-years away from Earth and spans 17.8 light-years. The cluster has 508 confirmed and 109 probable members and their combined mass is more than 285 solar masses.
Sh2-232
Sh2-232, also known as the Great Pumpkin Nebula, is a large, faint HII emission nebula located in the constellation Auriga, approximately 5,800 light-years from Earth. It is part of a larger complex of nebulae (including Sh2-235, Sh2-231 and Sh2-233) that are star-forming regions. Inside the nebula there is a small planetary nebula (PN G173.5+03.2). The planetary nebula also emits OIII, but Sh2-232 has no OIII signal of any significance. A total of two asteroids were discovered travelling through the Field of View
Caldwell 16
Caldwell 16, also known as NGC 7243, is an open cluster located 2,300 light years from Earth in the constellation of Lacerta. It was discovered in 1788 by William Herschel, contains an estimated 211 stars and has an angular diameter of about 21 arc minutes. The age of this cluster is estimated at about 250 million years. The cluster is fairly bright, with an apparent magnitude of 6.4 making it visible with the naked eye.
Caldwell 10
Caldwell 10, also known as NGC 663, is a young open cluster located 8,800 light years from Earth in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It has an estimated 400 stars and spans about a quarter of a degree across the sky. The star cluster is assumed to form part of the stellar association Cassiopeia OB8, that is located in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way, along with the open clusters M103, NGC 654, NGC 659, and some supergiant stars scattered between them, all of them having similar ages and distances.
Caldwell 8
Caldwell 8 (NGC 559) is an open cluster in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by William Herschel on 9 November 1787. About 120 stars populate the cluster, but only about 40 of them are of magnitude 12 or brighter. It is located near the open cluster NGC 637, and the bright magnitude +2.2 irregular variable star Gamma Cassiopeiae. The cluster is 7 arcmins across. The object is also called Ghost's Goblet.
Caldwell 22
Caldwell 22, also known as NGC 7662 or te blue snowball nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered on October 6, 1784 by William Herschel. Many photos focus on the bright core of the nebula itself. But there is a large envelope of faint OIII signal surrounding the nebula, which has been captured in this image as well.
Arp273
Arp 273 is a pair of interacting galaxies, 300 million light years away in the constellation Andromeda. The larger of the spiral galaxies, known as UGC 1810, is about five times more massive than the smaller galaxy, known as UGC 1813. It is thought that the smaller galaxy has actually passed through the larger one.
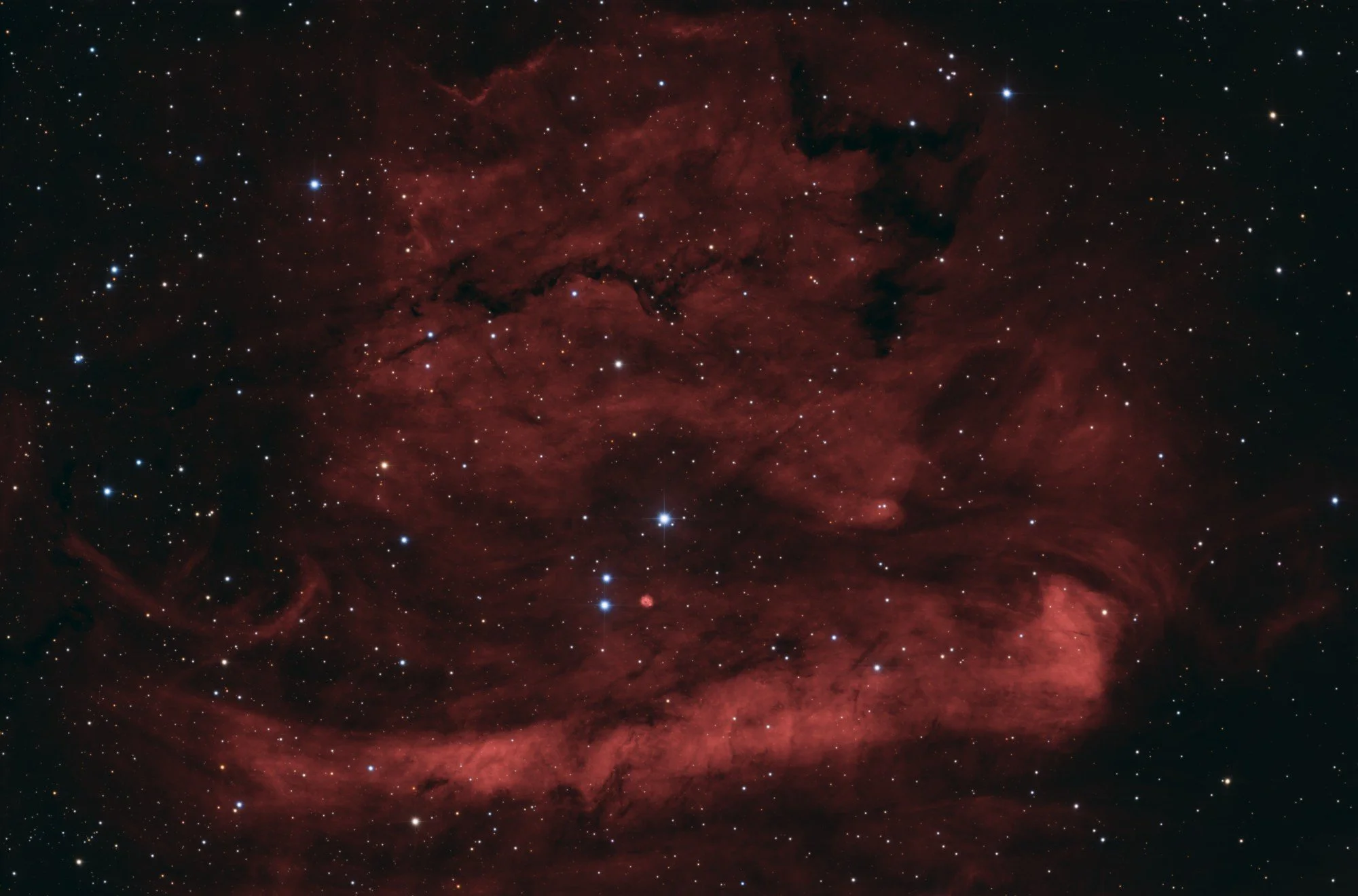
Sh2-231 | Sh2-233 | Sh2-235
A large HII region in the constellation Auriga contains four distinct Sharpless objects. Three of those (Sh2-231, Sh2-233 and Sh2-235) are imaged here. Sh2-235 is by far the brightest nebula in the area and shows a tiny bit of OIII signal in the nucleus. The other two objects are more typical Ha clouds.
Caldwell 1
Caldwell 1, also known as NGC 188 or the Polarissima Cluster, is an open cluster in the constellation Cepheus. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1825. Unlike most open clusters, NGC 188 lies far above the plane of the galaxy and is one of the most ancient of open clusters known, at approximately 6.8 billion years old.
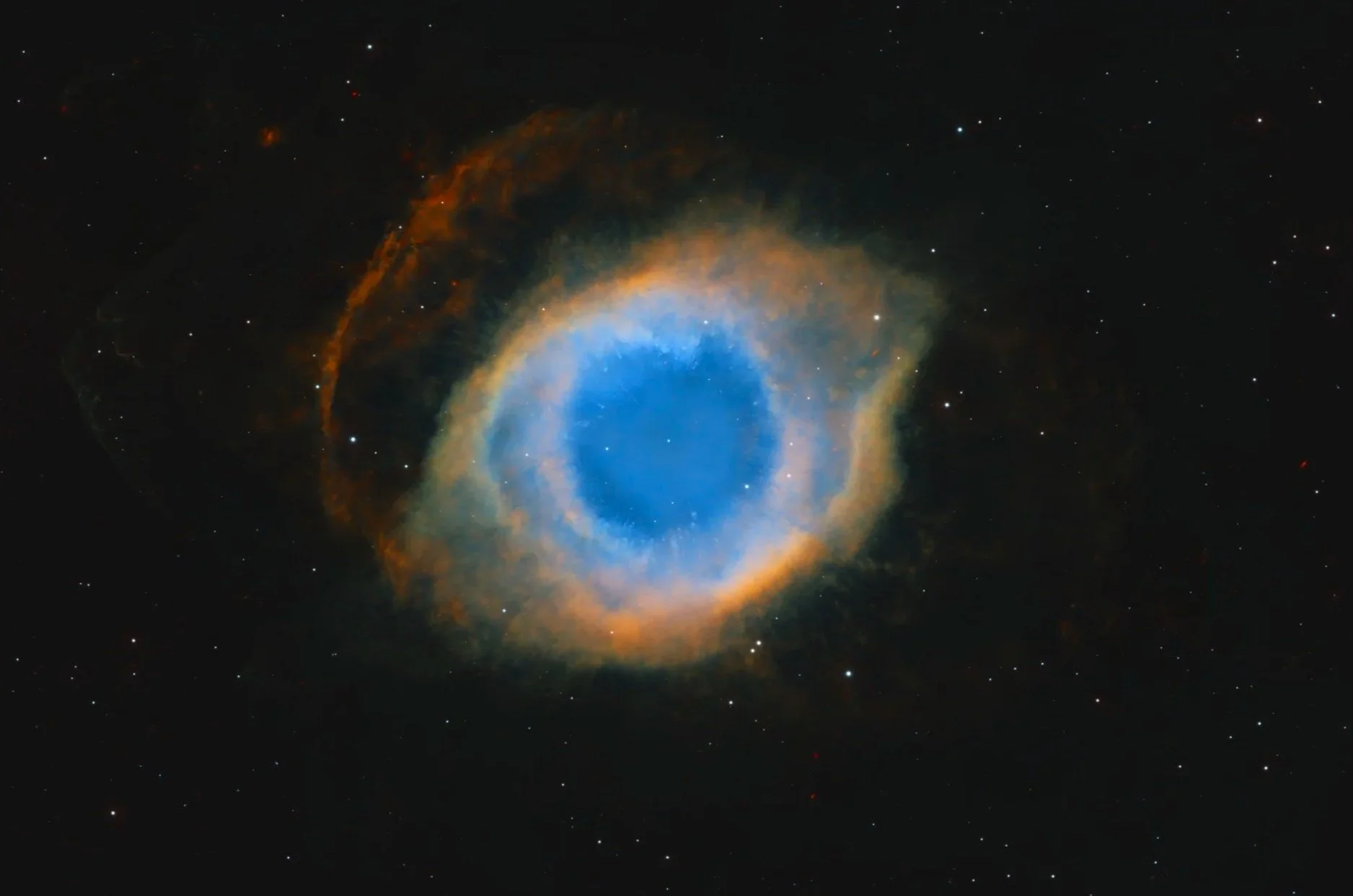
Caldwell 63
Caldwell 63, also known as NGC 7293 or the Helix Nebula, is a planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, most likely before 1824, this object is one of the closest of all the bright planetary nebulae to Earth. The distance, measured by the Gaia mission, is 655±13 light-years. Its age is estimated to be 10600 years. It is similar in appearance to the Cat's Eye Nebula and the Ring Nebula.
Caldwell 15
Caldwell 15, also known as NGC 6826 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Cygnus. It is commonly referred to as the "Blinking Planetary". A distinctive feature of this nebula are the two bright patches on either side, which are known as Fast Low-Ionization Emission Regions, or FLIERS. They appear to be relatively young, moving outwards at supersonic speeds. Caldwell 15 is located at approximately 2000 lightyears from Earth.
Caldwell 51
Caldwell 51, also known as IC 1613, is an irregular dwarf galaxy located on the outskirts of the Local group (the galaxy ground that includes our Milky Way) in the constellation of Cetus. Caldwell 51 was discovered in 1906 by Max Wolf, and is approaching Earth at 234 km/s.
M75
Messier 75 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included in Charles Messier's catalog that same year. M75 is about 67,500 light years away from Earth and is 14,700 light years away from, and on the opposite side of, the Galactic Center. Messier 75 is part of the Gaia Sausage, the hypothesised remains of a dwarf galaxy that merged with the Milky Way.
Caldwell 43
Caldwell 43 (also known as NGC 7814 or UGC 8) is a spiral galaxy about 40 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. The galaxy is seen edge-on from Earth. It is sometimes referred to as "the little sombrero", a miniature version of Messier 104. The star field behind NGC 7814 is known for its density of faint, remote galaxies. It's among the few bright galaxies that exhibit modest distortion and twisting of the galaxy's plane in optical wavelengths.
M72
Messier 72 is a globular cluster in the south west of the constellation of Aquarius. M72 was discovered by astronomer Pierre Méchain in 1780. Charles Messier looked for it 36 days later, and included it in his catalog. The cluster is approximately 55,000 lightyears away from the Sun. It has an estimated combined mass of 168,000 solar masses and is around 9.5 billion years old.